Water and wastewater treatment are critical for ensuring safe, sustainable water resources for municipal, industrial, and agricultural applications. These processes utilize advanced technologies such as filtration, adsorption, oxidation, and reduction to remove contaminants, including pathogens, chemicals, and emerging pollutants such as per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), disinfection byproducts (DBPs), pesticides and others. At Fraunhofer USA Center Midwest (CMW), we focus on developing and integrating innovative, cost-effective solutions, including the use of recycled materials and advanced treatment technologies, to enhance water quality, and environmental protection while ensuring regulatory compliance. Through continuous research and technological advancements, we drive the development of efficient, scalable, and sustainable water treatment solutions to address evolving global water challenges.
Water Treatment
Photolysis and Photocatalysis
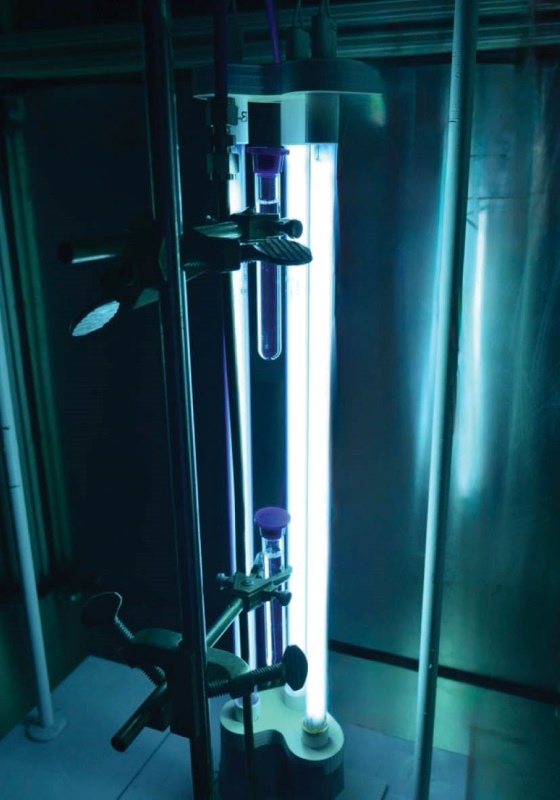

Photolysis and photocatalysis are advanced oxidation processes used in water treatment to degrade persistent contaminants in water including PFAS, DBPs and others. Photolysis involves the direct breakdown of pollutants using high-energy UV light, from UV lamp or natural sunlight. Photocatalysis, on the other hand, employs semiconductor materials (e.g., TiO₂) activated by UV or visible light to produce hydroxyl radicals, enhancing degradation efficiency of contaminants. At Fraunhofer USA CMW, we explore these techniques (e.g., UV/sulfite, VUV/UV, Solar/TiO2 and others) for efficient, cost-effective, and scalable water treatment solutions, focusing on contaminant mineralization to improve water quality while ensuring sustainability and regulatory compliance.
Adsorption
Adsorption is a widely used water treatment process that removes contaminants by binding them to the surface of porous materials. This method is highly effective for eliminating PFAS, and other emerging pollutants. At Fraunhofer USA CMW, we focus on developing cost-effective and sustainable adsorption technologies using recycled materials, to enhance pollutant removal. By optimizing adsorbent properties and treatment conditions, we aim to create high-capacity, regenerable, and scalable solutions for industrial and agricultural wastewater treatment. Our research integrates adsorption with other advanced treatment technologies to improve efficiency, reduce waste, and ensure long-term environmental sustainability. Current projects are funded by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) in collaboration with universities across the U.S., including the University of Maine, Michigan State University, and others, as well as in partnership with industry leaders such as Alro Steel and others.
Electrochemical Oxidation
Electrochemical oxidation (EO) is an advanced water treatment technology that degrades persistent contaminants through direct and indirect oxidation at the electrode surface. This process generates reactive species, such as hydroxyl radicals and reactive chlorine species, to break down pollutants like PFAS, pesticides, and DBPs. At Fraunhofer USA CMW, we are exploring EO as a highly efficient and scalable solution for industrial and agricultural wastewater treatment. By optimizing electrode materials and reaction conditions, we aim to enhance contaminant mineralization, energy efficiency, and long-term sustainability. Our work integrates EO with other advanced treatment technologies including sonolysis and photolysis to develop cost-effective, robust, and environmentally friendly water treatment solutions. Current and previous projects are funded in part through the state of Michigan in collaboration with Michigan State University, as well as in partnership with industry leaders.
➜ Chemical Sensing (Link to Page)
 Fraunhofer USA Center Midwest CMW
Fraunhofer USA Center Midwest CMW